Your payment security strategy must protect customer data at every step of the payment process. With 98% of merchants worldwide experiencing one or more types of fraud in the past 12 months, implementing comprehensive payment processing security best practices has never been more important within a payment processing system.
Why payment gateway security is critical in 2025
Keeping up with the surge of online transactions requires a comprehensive payment security strategy that starts at your payment gateway. Everything from instant payments to cross-border commerce have expanded cybercriminals’ opportunities to exploit your systems. Because of this, establishing a secure payment infrastructure has never been more important.
Rising threats in digital payments
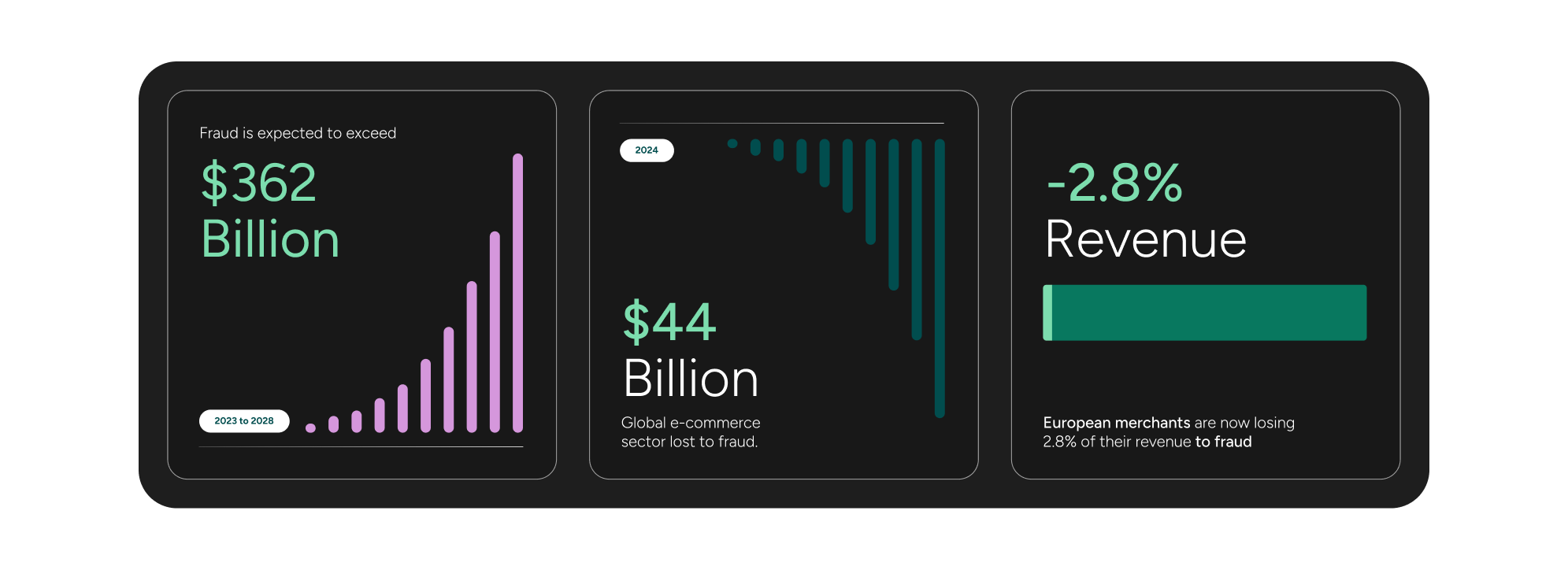
Sophisticated fraud schemes are targeting both consumers and merchants during nearly all online transactions. Data from McKinsey and Juniper Research shows that online payments fraud is expected to exceed USD 362 billion between 2023 to 2028. In 2024, the global ecommerce sector lost a staggering $44 billion to fraud – and the total is expected to surpass $100 billion by 2029. One study by Sift suggests that European merchants are now losing 2.8% of their revenue to fraud.
With fraudsters using AI and automation to enhance their attacks and social engineering tactics, maintaining a secure payment environment requires equally advanced defenses. To learn more, download our report ‘Fraud in Europe: Counting the cost for retailers and shoppers’ to find out more about how merchants can address the spike in scams.
“Leaders are spending valuable time dealing with the impact of fraud on their business, which in turn is creating significant administrative burdens that can be particularly burdensome for smaller merchants.” Oleg Stefanets, Chief Risk Officer, payabl.

Cost of a security breach
A breach can devastate a business financially and reputationally.
Although recent reports indicate that the cost of a data breach has decreased for the first time in five years, the global average cost of a breach still sits above USD 4 million.
Beyond immediate revenue loss, penalties, and legal exposure, companies face long-term damage to customer trust. Comparatively, strong payment security is far less costly than recovering from an incident. Prioritising your online payment security with protections like biometric authentication and tokenization can go a long way in keeping your customers and revenue safe.
Regulatory & compliance pressures
Compliance frameworks such as PCI DSS, PSD2, and evolving local laws place stricter requirements on how customer data is handled and protected. Businesses that prioritise compliance early strengthen both their credibility and their operational resilience.
Key payment gateway security architecture & design principles
Building a resilient payment security framework starts with designing a gateway architecture with in-depth defenses. A truly secure payment environment integrates multiple complementary layers that collectively minimize risk and ensure data integrity across every stage of a transaction.
Network segmentation & isolation
Effective gateway design begins with clear separation between public, application, and data layers, which in turn guarantees that no single breach can compromise the entire system. Isolated network zones reduce lateral movement risks and protect sensitive payment data against unauthorised access.
Encryption & tokenization across the flow
Strong encryption and tokenization protect data throughout its lifecycle. Encryption ensures confidentiality, while tokenization keeps sensitive information out of merchant systems entirely.
Secure APIs, microservices & gateway interfaces
API and microservice layers are designed with authentication, least-privilege access, and schema validation to prevent injection and spoofing attacks. They also include:
Secure key management
Keys are generated, stored, and rotated using certified HSMs to ensure cryptographic integrity.
Logging, monitoring & auditing layers
Visibility must span from front-end payment gateways to back-end payment processors, secured with transport layer security that can ensure traceability for rapid incident response.
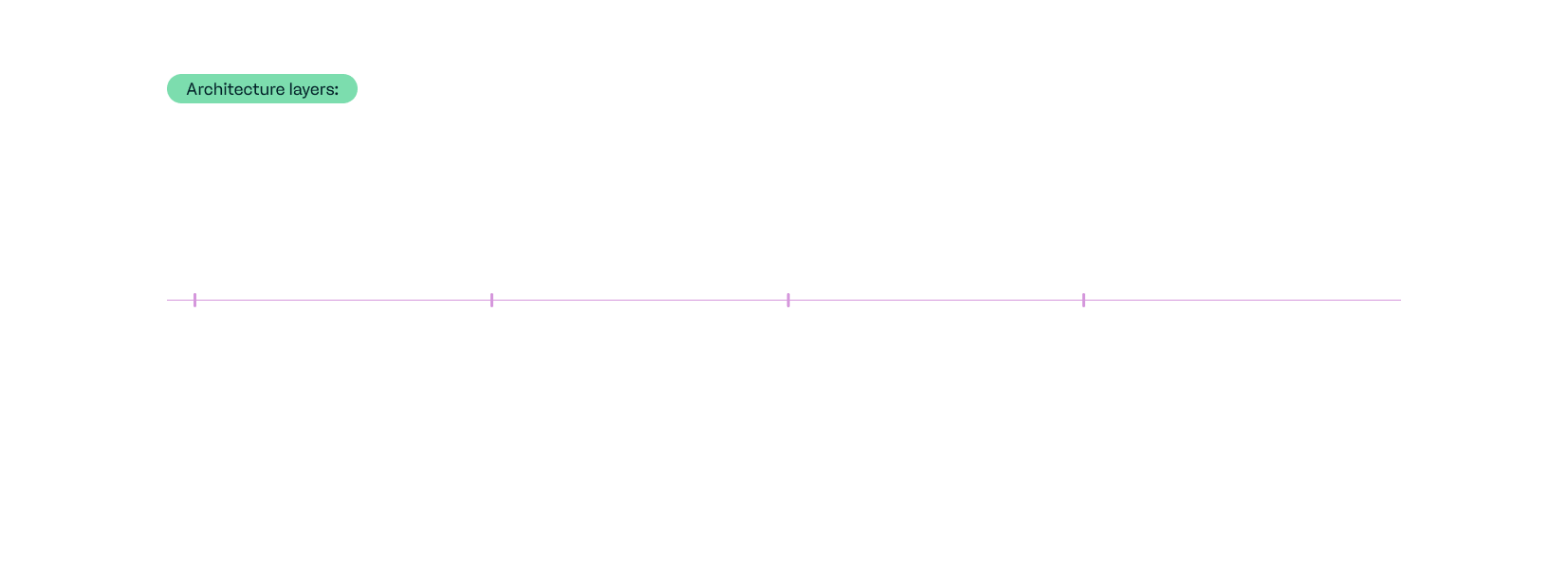
The architecture layers are as follows:
1. Data capture layer: Collects transaction and payment data from the payment gateway to be logged.
2. Logging layer: Normalises and routes transaction logs into a storage system.
3. Monitoring layer: Analyses patters, flags anomalies and triggers alerts.
4. Auditing layer: Maintains a permanent, tamper-proof record of transactions.
Common payment gateway security risks & vulnerabilities
Even the most secure payment gateways face persistent risks as hackers grow more sophisticated in their fraud attempts. Strong payment security requires continuous vigilance against both external and internal vulnerabilities that can lead to data loss, fraudulent transactions, and long-term harm to your business’s reputation.
Below are some of the most common and costly risks you must defend against:
- Data breaches & unauthorised access: Customer data remains a prime target in large-scale data breaches. Attackers exploit weak authentication or unpatched systems to steal personal and financial details, compromising your relationships with customers and regulators. Two factor authentication is a simple yet effective method for guarding your gateway from unauthorised access.
- Phishing, social engineering & credential theft: These tactics drive a significant share of payment fraud, tricking users into exposing sensitive data through deceptive messages or fake websites. The European Banking Authority reports that theft of card details via data breaches, phishing, and social engineering accounted for more than 60% of remotely initiated card fraud in 2023. Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) is a key standard for preventing these attacks.
- Account takeover & credential stuffing: Automated attacks reuse stolen passwords to gain control of user accounts, resulting in payment fraud and exposure of sensitive customer data.
- Card-not-present (CNP) fraud: A major source of credit card fraud, CNP attacks exploit online checkout systems, using stolen cardholder data to perform fraudulent transactions in digital environments. In the UK alone, CNP fraud accounted for roughly 70% of all card fraud losses in 2024, an 11% increase from the year prior.
- POS, malware & skimming attacks: Malicious software and hardware skimmers compromise in-store terminals, capturing sensitive data directly from POS devices.
- API & endpoint vulnerabilities, injection, & man-in-the-middle: Unsecured APIs or poor encryption can expose gateway communications to interception and manipulation.
- Insider threats & misconfigurations: Human error and poor access control often lead to accidental leaks or intentional misuse of privileged systems, undermining even the strongest defenses.
- Friendly fraud: Friendly fraud is caused by customers disputing legitimate charges despite receiving the product or service. It can happen both intentionally and unintentionally, making it difficult to identify and counteract. Across the EMEA and APAC regions, 59% of ecommerce merchants report experiencing increased friendly fraud attacks.
Payment gateway & processing security standards, compliance & requirements
PCI DSS
Payment security standards continue to evolve from the legacy PA-DSS, which guided payment application development, to the modern PCI Software Security Framework (SSF). Together with PCI DSS, these frameworks establish comprehensive requirements for payment processing security standards.
ISO/SOC/local regulations/data protection
Global frameworks like ISO 27001 and SOC 2 complement regional regulations such as GDPR and PSD2 SCA to create a more comprehensive web of data governance and payment security. These standards collectively mandate strong authentication, encryption, and accountability measures to protect personal and financial data across jurisdictions and digital payment environments.
PCI DSS vs. ISO 27001
| Differences | PCI DSS | ISO 27001 |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory scope | Narrow in scope, focusing specifically on entities that handle payment card data, such as merchants and payment processors. | Covers all forms of information and data across any industry. Applicable to all organisations, regardless of size or sector. |
| Compliance requirements | PCI DSS imposes specific and prescriptive controls designed to protect payment card data throughout the entire payment process, including encryption, access control, and network monitoring. For example, to meet the multi-factor authentication requirement, you must provide two of three authentication methods, such as a password, a token device, or biometric authentication like a fingerprint. | The main requirement is the establishment of an information security management system (ISMS) and risk-based controls for protecting sensitive data. Requirements are flexible and process-driven. |
| Certification | PCI DSS compliance certification is mandatory for all businesses that handle payment card data, but the exact certification requirements depend on a company’s PCI level (more on that later). | ISO 27001 is a voluntary certification that can be earned by demonstrating a strong information security posture through a third-party audit. |
Industry best practices & security standards
Adopting recognised frameworks like OWASP and NIST helps you achieve a secure payments environment and develop ongoing resilience against modern threats. With these frameworks, you can ensure your payment gateways and other support systems remain protected against evolving cyber threats and compliance requirements.
Core payment gateway security best practices & features
As cyber threats grow more advanced, businesses can’t afford to rely on outdated security frameworks or reactive protection protocols. Modern payment gateways must combine multiple layers of defense ranging from advanced encryption and tokenization to intelligent fraud detection.
Let’s break this down further by exploring the seven key payment security best practices we employ at payabl. and that you should seek from any provider you partner with:
1. Tokenisation & encryption
Data encryption and tokenization ensure that sensitive information never appears in a readable format, whether at rest or in transit.
Tokenisation replaces actual card data with unique, randomly generated tokens, eliminating the risk of exposing personal payment details during storage or transfer. Meanwhile, encryption ensures that even if intercepted, data remains unintelligible without the correct decryption keys.
For example, our debit and credit card tokenization solutions are backed by our PCI Level 1 compliant proprietary gateway.
2. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) & strong identity controls
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an essential extra step that requires users to confirm their identity through a secondary factor such as a one-time code or biometric verification.
At payabl., we combine our fraud prevention tools with 3D Secure and custom fraud rules to create a tailored environment that keeps you and your customers safe, always.
3. Real-time transaction monitoring & fraud detection engines
Your internal payment gateway security requirements should mandate continuous transaction monitoring and the use of advanced fraud detection engines and rule-based logic to catch threats early.
Looking at our own AI-powered fraud engine as an example, it works in four key ways:
- Instant evaluations of transactions through Sift’s machine learning engine
- Real-time analyses of risk signals from devices, customer behaviors, and geographic locations
- Seamless approvals of safe transactions, paired with blocking or flagging mechanisms for high-risk transactions
- Central management of exceptions and disputes from the payabl.one dashboard
4. Device/terminal hardening & secure hardware elements
In physical payment environments, endpoint protection is just as important as backend encryption.
Our POS terminals are built using secure hardware elements that handle sensitive operations such as key generation and cryptographic storage. We also follow industry standards for device hardening, ensuring tamper resistance, encrypted boot sequences, and automatic data erasure upon intrusion detection. Regular firmware updates and remote monitoring can maintain your device integrity and protect against exploits that target POS systems and IoT endpoints.
5. API rate limiting, throttling, and WAFs
APIs are essential components of modern payment systems, but they can also be a potential point of entry for experienced hackers. You need a payment gateway provider that incorporates strict API rate limiting and throttling policies designed to prevent abuse from both human and bot-based attackers.
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) adds another layer of critical protection by filtering malicious traffic and monitoring for cross-site scripting attempts. Every request is authenticated and logged, allowing rapid response in case of suspicious activity.
At payabl., our secure API allows for even more payment security features, such as a pre-authorisation interface that verifies credit card data and credit lines before reserving the requested funds.
Read our full API documentation here.
6. Secure software development lifecycle (SSDLC), code reviews & penetration testing
An SSDLC integrates security features into every aspect of software design. In practice, this translates into additional security checks, code reviews, and independent penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities early in the development process.
Prioritising security by design ensures that any potential issues are resolved before they ever reach production, keeping your reputation safe from harm and your customers’ data protected.
7. Data minimisation & retention policies
Strong security practices center around taking responsibility.
Strict data minimization that collects only what is necessary and retains it only as long as required by regulation or business need is an absolutely necessary practice. Likewise, sensitive data should be anonymised or purged according to predefined schedules, minimising exposure over time.
Our approach to payment security at payabl. is simple: minimise risks, maximise trust, and protect transactions end to end.
Payment gateway security testing & validation checklist
Use the following checklist to align your business with current payment gateway security standards and build resilience against sophisticated threats:
- Vulnerability scanning & pen testing: Conduct automated scans and manual penetration tests regularly. A fully secure system shows no exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Threat modeling & attack surface analysis: Map all potential attack vectors to demonstrate you have a secure environment that minimises exposure and enforces least-privilege access.
- API/endpoint fuzzing & security testing: Continuously test APIs for input validation and data leakage. Your gateway should be able to properly handle malformed or unexpected requests.
- Penetration testing (internal/external): Perform both insider and outsider attack simulations to test whether your gateway can withstand intrusion attempts without compromising data.
- Code audits & static/dynamic analysis: Review code for logic flaws and unsafe dependencies, verifying that your applications maintain clean, verified builds.
- Red-teaming/chaos engineering (for resilience): Stress-test production-like systems under failure conditions to build greater resilience. A secure infrastructure can maintain uptime and prevent cascading breakdowns in payment processing app security.
How to evaluate & choose a secure payment gateway provider
When it comes to choosing a payment gateway provider, you must find a technological partner that can balance performance with security. A provider with robust security features can process transactions efficiently while keeping sensitive data protected through layered defenses.
Start by assessing the following features:
Security feature checklist
- Evaluate the provider’s encryption and/or tokenization protocols
- Prioritise providers that offer advanced fraud detection and authentication controls
- Confirm payment processing security compliance with standards like PCI DSS, ISO 27001, and SOC 2 certifications.
SLA, audit reports, certifications, 3rd-party assessments
Review SLAs, independent audit reports, and third-party assessments to verify ongoing compliance with current payment gateway security standards.
Vendor reputation, incident history & transparency
Investigate public breach disclosures and how effectively these incidents were managed. A trustworthy provider maintains transparency and communicates security updates proactively.
Integration, extensibility, and security trade-offs
Assess how easily a payment gateway solution integrates with your existing stack.
The best security features of payment gateway providers deliver flexibility and innovation without compromising data protection or compliance.
Case studies & real-world examples
Breach case study
- Background: In 2018, British Airways experienced a data breach that compromised payment card data of more than 400,00 customers, resulting in a £20m fine.
- What went wrong: While the exact technical exploits have not been publicly released, it is suspected that a malicious piece of code on the BA website was responsible for the breach.
- Lessons learned: The British Airways breach is a classic example of a supply chain attack that could have been prevented through stricter data storage protocols and better adherence to PCI DSS standards.
Success case study
- Background: CVS Health accidentally exposed more than 1 billion search records in 2021, including customer email addresses and user IDs, making this data readily available to the public.
- What went right: An independent cybersecurity researcher discovered the leak and alerted the company, who promptly secured a misconfigured database responsible for the leak.
- Lessons learned: Internal testing is rarely enough. To keep your systems and data safe, it is crucial to also engage with independent, third-party assessments.
Summary
Effective payment security requires a comprehensive approach that protects customer data across all stages of a transaction. The payment processing security best practices you implement should include:
- Encryption and tokenization
- Multi-factor authentication
- Real-time monitoring
- Continous testing
Choosing a provider with proven secure payment features, transparent policies, and rigorous testing ensures resilience against increasingly sophisticated threats.
Contact payabl. today to get your free security assessment.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
How do I know if a payment gateway is secure?
Check your payment gateway provider’s certifications with frameworks like PCI DSS and ISO 27001.
Which payment gateway is most safe?
payabl.checkout offers a highly secure payment gateway solution with support for over 300 global payment methods.
How to check security testing?
Look for a provider that conducts regular vulnerability scans, penetration tests, API fuzzing, code audits, and independent third-party audit reports.
What are the 4 levels of PCI compliance?
Level 1: Businesses that process over 6 million card transactions per year
Level 2: Businesses that process between 1 million and 6 million card transactions per year
Level 3: Businesses that process between 20,000 and 1 million card transactions per year
Level 4: Businesses that process fewer than 20,000 card transactions per year
What are PCI compliance requirements?
PCI compliance requirements vary depending on your level. Read payabl.’s PCI DSS compliance guide for more information.